
Piriformis syndrome is a condition causing hip and buttock pain due to tightness or irritation of the piriformis muscle. It’s often mistaken for sciatica but can be effectively managed with targeted stretches and exercises to relieve discomfort and improve mobility.
What is Piriformis Syndrome?
Piriformis syndrome is a condition characterized by pain in the hip and buttock region, caused by tightness or irritation of the piriformis muscle. This muscle, located deep in the buttocks, plays a key role in hip rotation and stability. When it becomes inflamed or spasms, it can compress the nearby sciatic nerve, leading to symptoms similar to sciatica. Activities like prolonged sitting, running, or repetitive hip movements often exacerbate the condition. While it is sometimes overlooked in diagnoses, piriformis syndrome is treatable with targeted stretches, exercises, and physical therapy. Early intervention is crucial to alleviate discomfort and restore normal hip function.
Common Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms of piriformis syndrome include pain in the buttocks and hips, often radiating down the back of the leg. This pain may worsen with sitting, coughing, or activities like running. Tenderness over the piriformis muscle and limited hip movement are also typical. Diagnosis involves physical exams, such as the Freiberg and Pace tests, to assess muscle tightness and pain. Imaging like MRI or ultrasound may be used to rule out other conditions, such as a herniated disk. Sciatica-like symptoms can make diagnosis challenging, but targeted exams help differentiate piriformis syndrome from other causes of hip and leg pain.
The Role of Stretching in Treatment
Stretching plays a crucial role in treating piriformis syndrome by relieving muscle tightness and improving hip mobility. Targeted stretches, such as the Figure-4 stretch and seated piriformis stretch, help alleviate sciatic nerve compression caused by a tight piriformis muscle. Regular stretching can reduce pain and stiffness, enabling better movement and posture. Consistency is key, as daily stretching routines promote long-term relief and prevent recurrence. Proper technique is essential to avoid aggravating the condition, so starting slowly and gradually increasing intensity is recommended. By incorporating these stretches into a daily regimen, individuals can effectively manage symptoms and enhance overall hip function, reducing discomfort and improving quality of life.
Understanding the Piriformis Muscle
The piriformis muscle is a small, deep muscle in the buttocks that plays a key role in hip rotation and stability. It is located near the sciatic nerve.
Location and Function of the Piriformis Muscle
The piriformis muscle is located deep within the buttocks, originating from the anterior surface of the sacrum and inserting on the greater trochanter of the femur. Its primary function is to stabilize the hip joint and assist in external rotation of the hip when extended, as well as abduction when the hip is flexed. This muscle plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and posture. Due to its proximity to the sciatic nerve, tightness or irritation of the piriformis can lead to discomfort and mobility issues. Understanding its anatomical position and function is essential for effective stretching and treatment of related conditions like piriformis syndrome.
How the Piriformis Muscle Relates to the Sciatic Nerve
The piriformis muscle is situated near the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down to the legs. In some individuals, the sciatic nerve can pass through or alongside the piriformis muscle, making it susceptible to compression. When the piriformis muscle becomes tight or inflamed, it can press against the sciatic nerve, leading to pain and discomfort often associated with piriformis syndrome. This compression can mimic symptoms of sciatica, such as radiating pain down the back of the leg. Stretching and releasing tension in the piriformis muscle are key to alleviating this pressure and restoring normal function to the sciatic nerve, thereby reducing pain and improving mobility.
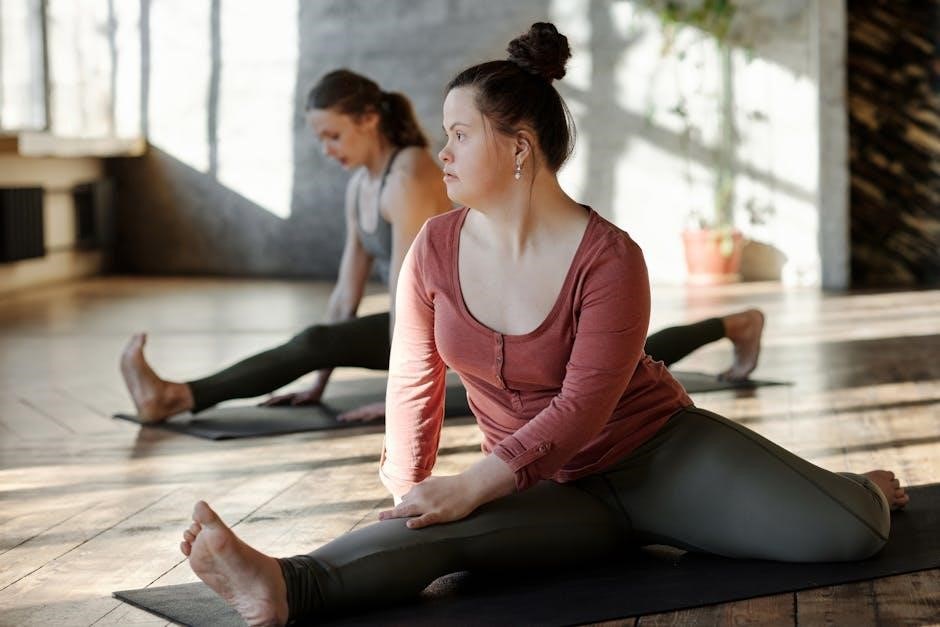

Best Stretches for Piriformis Syndrome
Effective stretches like the Figure-4, seated piriformis, bridge pose, and foam roller glute stretches target the piriformis muscle, relieving pain and improving hip mobility.
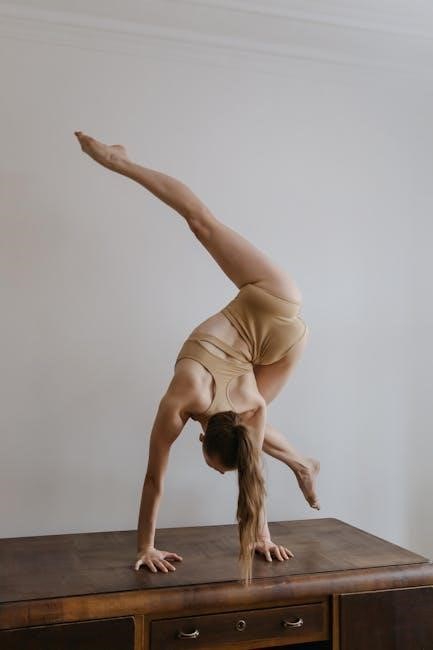

Figure-4 Stretch for Hip Flexibility
The Figure-4 stretch is a highly effective exercise for hip flexibility, specifically targeting the piriformis muscle. To perform this stretch, lie on your back and cross one foot over the opposite knee, forming a “4” shape. Gently pull the unaffected leg toward your chest until a mild stretch is felt in the buttock area. Hold this position for 20-30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times on each side. This stretch helps release tension in the piriformis muscle, reducing pain and improving hip mobility. It is essential to breathe deeply and avoid bouncing to ensure a safe and effective stretch.
Seated Piriformis Stretch
The seated piriformis stretch is an excellent exercise for targeting the piriformis muscle while maintaining proper posture. To perform this stretch, sit on the floor with your legs extended straight. Cross the affected leg over the other thigh, placing the foot on the ground. Gently press down on the knee of the crossed leg with your hand until a mild stretch is felt in the buttock area. Hold this position for 20-30 seconds and repeat 2-3 times on each side. This stretch helps relieve tightness and improve hip mobility, making it particularly effective for those with piriformis syndrome; Ensure deep breathing and avoid bouncing to maximize the benefits of this exercise;
Bridge Pose for Piriformis Relief
Bridge pose is a simple yet effective stretch for alleviating piriformis syndrome symptoms. To perform this exercise, lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground. Slowly lift your hips toward the ceiling, squeezing your glutes at the top of the movement. Hold this position for 5-10 seconds before lowering your hips back down. Repeat this motion 10-15 times. This stretch helps relieve tension in the piriformis muscle and improves hip flexibility. It is essential to maintain proper form by keeping your knees aligned with your toes and avoiding any pain during the movement. Deep breathing can enhance the relaxation benefits of this pose, making it an excellent addition to your daily stretching routine for piriformis relief.
Foam Roller Glute and Piriformis Stretch
Using a foam roller is an excellent way to target the glutes and piriformis muscle for relief from tightness and pain. Place the foam roller on the floor and position yourself so the roller is under your glutes. Slowly roll back and forth, applying gentle to moderate pressure. Focus on areas that feel tender or tight, stopping periodically to hold pressure on these spots for 20-30 seconds. This technique helps break up muscle adhesions and improves circulation. To enhance the stretch, lift one leg toward the ceiling and roll through the affected area. Regular use of a foam roller can significantly reduce piriformis muscle tension and alleviate discomfort associated with piriformis syndrome. Always prioritize gentle movements and avoid applying too much pressure, which could cause further irritation.
Exercises Beyond Stretching
Beyond stretching, exercises like foam rolling and dynamic warm-ups help improve hip mobility and reduce muscle tension, providing comprehensive relief from piriformis syndrome symptoms.
Foam Rolling for Deep Tissue Mobilization
Foam rolling is an effective method for deep tissue mobilization, targeting the piriformis muscle and surrounding areas. By lying on a foam roller positioned under the glutes, you can gently roll back and forth, applying pressure to release tension. This technique helps break up adhesions and knots, improving blood flow and reducing muscle tightness. Start slowly, focusing on sore spots, and hold pressure for 20-30 seconds to allow relaxation. Foam rolling can be particularly beneficial for those with piriformis syndrome, as it enhances flexibility and eases discomfort without overstretching. Regular use can also aid in preventing future flare-ups by maintaining muscle balance and promoting recovery.
Dynamic Warm-Up Exercises for Hip Mobility
Dynamic warm-up exercises are essential for improving hip mobility and preventing piriformis syndrome. Start with leg swings, both forward-backward and side-to-side, to loosen the hip joints. Next, perform hip circles by standing with feet shoulder-width apart and moving the hips in large circles, first clockwise and then counterclockwise. Lunges with a twist can also help stretch the piriformis muscle while enhancing flexibility. These exercises promote blood flow, reduce muscle stiffness, and prepare the hips for more intense activities. Incorporating dynamic warm-ups into your routine can significantly improve range of motion and reduce the risk of discomfort or injury. They are simple, effective, and can be adapted to suit different fitness levels, making them a great addition to any workout or rehabilitation program.

Prevention and Maintenance
Preventing piriformis syndrome involves regular stretching, strengthening core muscles, and maintaining proper posture. Incorporating dynamic warm-ups and cool-downs can reduce muscle tightness and improve overall hip mobility effectively.
Importance of Regular Stretching and Exercise
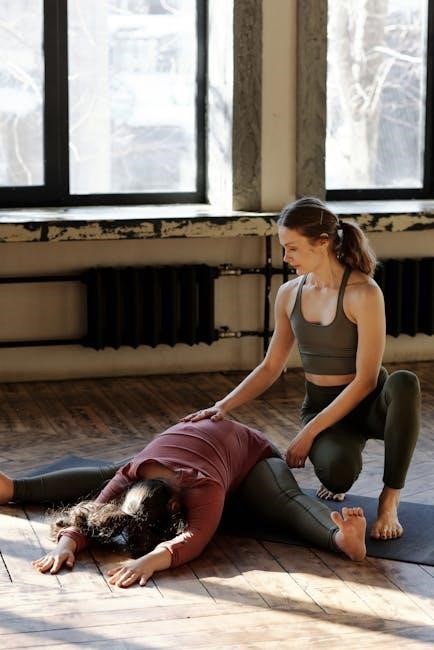

Regular stretching and exercise are crucial for managing piriformis syndrome, as they help reduce muscle tightness and improve hip mobility. Gentle stretches like the figure-4 and seated piriformis stretches can alleviate symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Strengthening exercises for the glutes and core muscles also play a key role in stabilizing the hip joint and reducing strain on the piriformis muscle. Consistency is important, as irregular exercise may lead to recurring pain. A physical therapist can tailor a program to address specific needs, ensuring exercises are performed safely and effectively. Over time, regular practice enhances flexibility, strength, and posture, reducing the risk of future episodes and promoting long-term relief from piriformis syndrome symptoms.
Posture and Movement Awareness
Maintaining proper posture and movement awareness is essential for managing piriformis syndrome. Poor posture, such as slouching or leaning unevenly, can strain the piriformis muscle and exacerbate symptoms. Being mindful of body positioning during daily activities, like sitting or lifting, helps reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve. Avoiding repetitive motions and adopting ergonomic practices can prevent muscle tightness. Additionally, incorporating exercises that promote body awareness, such as yoga or Pilates, can improve alignment and reduce discomfort. Regularly assessing and correcting posture ensures long-term relief and prevents recurrence of piriformis syndrome. By fostering awareness of how you move and position your body, you can create a healthier environment for your muscles and joints, enhancing overall mobility and comfort.

When to Seek Professional Help
Consult a physical therapist if experiencing severe pain, limited mobility, or worsening symptoms despite self-care. Professional guidance ensures proper treatment and prevents further complications.
Signs That You Need to Consult a Physical Therapist
If you experience persistent pain in the buttocks or hips that doesn’t improve with self-stretching, it may be time to seek professional help. A physical therapist can assess your symptoms and create a personalized treatment plan. Key signs include difficulty sitting for long periods, pain when walking or climbing stairs, and radiating pain down the leg. If you notice numbness or tingling, it could indicate nerve involvement, requiring expert intervention. A therapist will guide you through targeted exercises and manual therapy to alleviate symptoms and improve mobility. Early consultation can prevent long-term damage and enhance recovery. Don’t hesitate to seek help if pain disrupts daily activities or worsens over time.